Power generation
Electrical Energetics
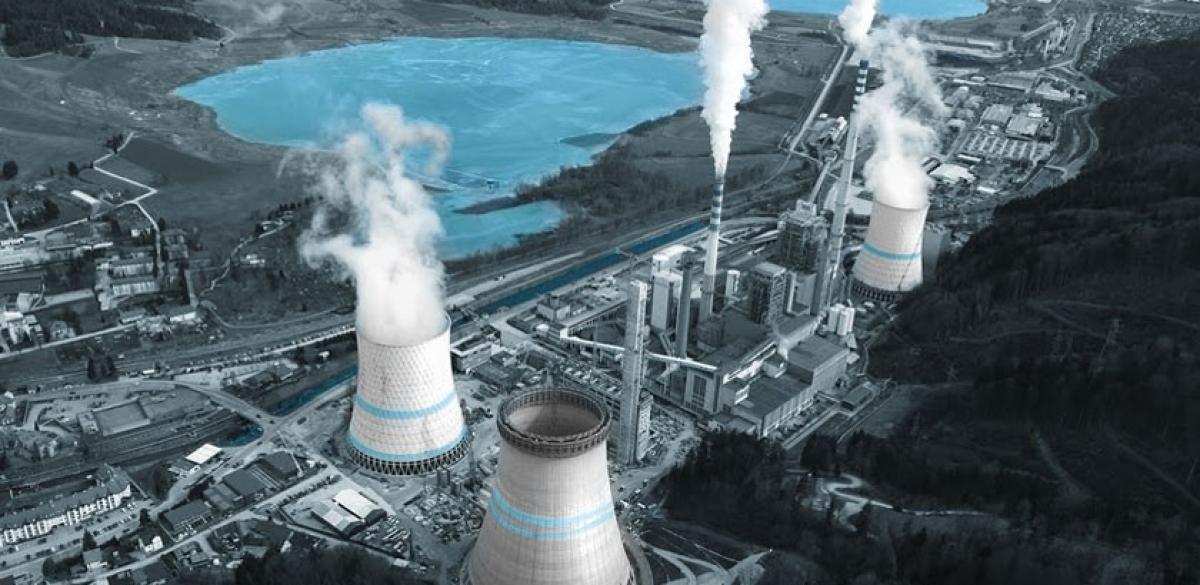

The modern world runs on electrical power. It is efficient to generate it industrially and at large scale, using easily accessible resources. Using electrical induction to generate three-phase alternating current is the strongly prevalent method. Electrical generators are essentially motors in reverse: they transform external mechanical power to electrical energy. Traditionally, steam or water is used to drive a turbine that turns the rotor.
The electrical part of the plant operates at high, alternating voltage. This means electrical safety must be at a commensurately high level to protect workers. Any bystanders are discouraged by fences and other physical barriers. The grounding system is the most important safety component of a high voltage installation. Methods for testing it will be considered in more detail in the application notes following this introduction.
Apart from voltage generation, the plant also contains the primary transformers and switchyards necessary to transferring the power to transmission and distribution. In the case that it is connected to high voltage DC network, the DC conversion will also be part of the same facility.
The basic and most important safety measure is the earthing/grounding system. Different approaches are used. They depend on the voltage magnitude and frequency used in the generation. Lightning protection must be particularly robust since power generation is an essential service. The high-voltage equipment must be well isolated and removed from any personnel. Equipotential planes in the vicinity of the facility must be considered. Step and touch voltages can be dangerous even at fair distance from the voltage source. Power quality of the generator and its supporting structures need constant monitoring.
Electrical power generation can be fuelled by different sources. Most common are heat from fuel, nuclear reaction or sun, and potential energy of water. Each has specific but related electrical safety issues that need consideration. Primary transformers and possible DC conversion are a separate issue.
Metrel solutions can help with design, erection, troubleshooting and maintenance of any protective measure in high-voltage installation environment.
Application Notes
Competencies at edison
EDISON is an international organisation for certification of competences in electrical safety testing. Click on the links for more information on each competency.
- EEA: Electrical Energy systems
- EES: Earthing and grounding systems
- PQA: Power quality analysis
- IEEE 81-2012 IEEE Guide for measuring earth resistivity, ground impedance, and earth surface potentials of a grounding system
- EN 50522 Earthing of power installations exceeding 1 kV a.c.
- IEC 62305 Protection against lightning
- IEC 60364-6 Low voltage electrical installation safety: Part 6 Verification.
- IEC 60909 Short-circuit currents in three-phase a.c. systems
- IEC 60947-2 Low-voltage switchgear and controlgear – Part 2: Circuit-breakers
- IEEE 519 Reporting and evaluating of the results
- EN 50160 Voltage quality reporting and evaluating of the results
- IEC 61000-4-30/-7/-15 – Power quality measurement methods, testing and measurement techniques