Patient recovery rooms and hospital wards
Medical Facilities
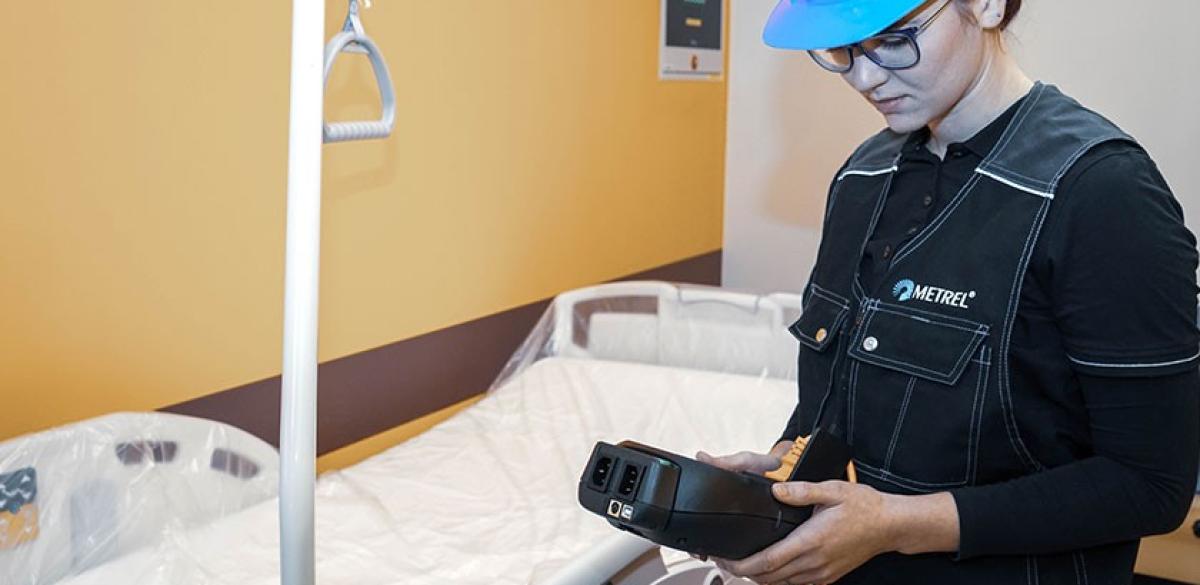

Patient recovery areas are a diverse group of places, both indoor and out. They can include everything from hospital rooms to swimming pool or parks and other green spaces. Rules of electrical safety are similar in all of them, as they are all considered public places.
Wet places are defined as unprotected from the weather or exposed to liquids, water or moisture to considerable degree. Such conditions occur in multiple places in a hospital and in patient areas: park lighting, any part of a wellness and recovery centre, surgery room, bathrooms and kitchen. Rooms can also be considered partially wet.
Wet skin is a much better conductor than dry, and sweaty or otherwise salty skin is even better. Contact voltage and leakage current must therefore be significantly lower. Insulation of any electrical equipment in or close to the water must be particularly high and always in good condition. The installation is kept as far away from the water as possible, or mechanically protected from it.
In dry areas only the items or parts that are large enough to be gripped or can contact a significant area of the body surface are considered. Smaller parts are less dangerous even if they do become live. Touching them will cause the muscle to contract away from them and break the contact. Inside a single building, it is also important to have all the protective earth wires at the same potential. For example a communication or computer system that can be constructed entirely separately must still have a protective connection to the common potential.
Public places and workplaces are similar in their general intention: they are both filled with people who are not themselves responsible for the state of installations they use (except in the sense of avoiding damaging it). Workplaces usually contain some electrical appliances or machines that need special care, and the employees are instructed in their use. Safety of the installation is however established with the same set of measurements as for public space, as required by the standard families IEC 60364 and IEC 61439. Measuring equipment used is covered by IEC 61557. Measurements have to be performed by an authorized inspector. Commissioning and periodic tests are mostly the same. Commissioning contains some extra points in the visual examination, before they are covered by décor, furniture or appliances.
A large majority of public places and workplaces has TT or TN grounding system, which means a low or very low PE resistance. The working voltage is measured between phase and neutral conductors. Measurements include earth resistance, lightning protection, surge protection and equipotential bonding (see other notes), insulation resistance, leakage currents, impedances in the lines and short-circuit currents, and RCD functionality.
The main way of determining safety, even with these electrical test available, is still visual inspection. Every accessible part of the installation has to be visually checked for adequacy and signs of degradation or corrosion. Great majority of problems is discovered visually. It includes everything from checking compliance to wire colours and warning inscription regulations.
Competencies at edison
EDISON is an international organisation for certification of competences in electrical safety testing. Click on the links for more information on each competency.
- MEDi: Medical and Surgery Rooms Electrical Installations Safety
- MEDe: Medical Electrical Equipment Safety
- EISinsp: Low Voltage Electrical Installation Safety for Inspectors
- IEC / EN HD 60364-7-710 Low-voltage electrical installations
- Part 7-710: Requirements for special installations or locations – Medical Location
- IEC EN 61557 – 8 Insulation monitoring devices for IT systems
- IEC / EN 62353 Medical Electrical Equipment – Recurrent test and test after repair of medical electrical equipment
- IEC / HD 60364-6 Low Voltage Electrical Installation Safety: Part 6 Verification